HTTP Signature for Webhooks
When receiving webhooks, it's important to verify that the payload is sent by a trusted source and has not been tampered with. This is commonly achieved by using an HTTP signature, where the sender signs the payload using a secret key and a hashing algorithm (e.g., SHA256). The receiver can then verify the signature using the same secret key.
How HTTP Signature Works
-
Sender Side (Webhook Provider):
- The payload (usually the request body) is hashed using HMAC with SHA256 and a shared Webhook Secret Key.
- The resulting signature is sent in a header (
HTTP-WEBHOOK-SIGNATURE).
-
Receiver Side (Your Server):
- Upon receiving the webhook, your server computes the HMAC SHA256 hash of the received payload using the same Webhook Secret Key.
- It compares the computed signature with the one provided in the header.
- If they match, the payload is authentic.
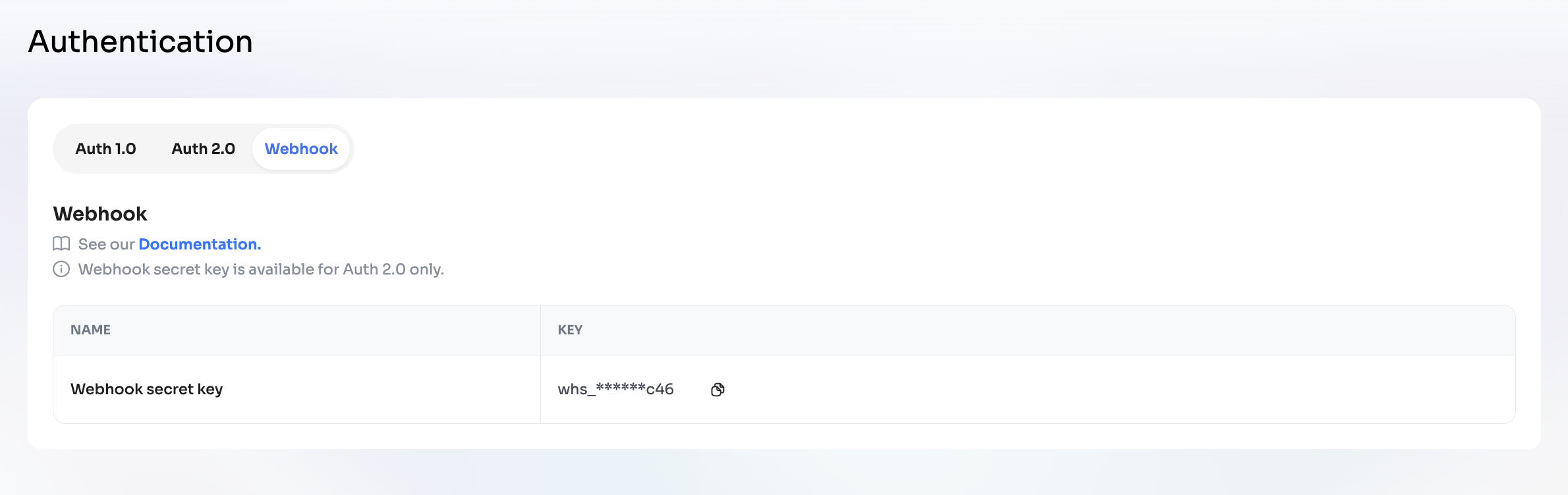
Where to find your Webhook Secret Key
You can retrieve your Webhook Secret Key in the Dashboard:
- Go to Dashboard → Developer → Authentication → Webhook tab.
- Copy the key from the field Webhook secret key.
- Use this key to generate and verify signatures.
Example: Generating & Verifying HTTP Signature
- Node.js
- Java
- Ruby
- C#
- Go
- Python
const crypto = require('crypto');
function generateSignature(payload, webhookSecretKey) {
return crypto
.createHmac('sha256', webhookSecretKey)
.update(payload, 'utf8')
.digest('hex');
}
// Example usage:
const payload = JSON.stringify({ foo: 'bar' });
const webhookSecretKey = 'your_webhook_secret_key_here';
const signature = generateSignature(payload, webhookSecretKey);
console.log('Signature:', signature);
// Verifying
const receivedSignature = req.headers['HTTP-WEBHOOK-SIGNATURE'];
const expectedSignature = generateSignature(req.rawBody, webhookSecretKey);
if (receivedSignature === expectedSignature) {
// valid
} else {
// invalid
}
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class WebhookSignature {
public static String generateSignature(String payload, String secret) throws Exception {
Mac sha256_HMAC = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
SecretKeySpec secret_key = new SecretKeySpec(secret.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), "HmacSHA256");
sha256_HMAC.init(secret_key);
byte[] hash = sha256_HMAC.doFinal(payload.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
StringBuilder hexString = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : hash) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(0xff & b);
if(hex.length() == 1) hexString.append('0');
hexString.append(hex);
}
return hexString.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String payload = "{\"foo\": \"bar\"}";
String secret = "your_webhook_secret_key_here";
String signature = generateSignature(payload, secret);
System.out.println("Signature: " + signature);
// Verifying
String receivedSignature = "signature_from_header";
if (receivedSignature.equals(generateSignature(payload, secret))) {
System.out.println("Valid");
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid");
}
}
}
require 'openssl'
payload = '{"foo": "bar"}'
webhook_secret_key = 'your_webhook_secret_key_here'
signature = OpenSSL::HMAC.hexdigest('sha256', webhook_secret_key, payload)
puts "Signature: #{signature}"
# Verifying
received_signature = request.headers['HTTP-WEBHOOK-SIGNATURE']
expected_signature = OpenSSL::HMAC.hexdigest('sha256', webhook_secret_key, request.raw_post)
if received_signature == expected_signature
puts "Valid"
else
puts "Invalid"
end
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
class Program {
static string GenerateSignature(string payload, string secret) {
var key = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(secret);
var message = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(payload);
using (var hmac = new HMACSHA256(key)) {
var hash = hmac.ComputeHash(message);
return BitConverter.ToString(hash).Replace("-", "").ToLower();
}
}
static void Main() {
string payload = "{\"foo\": \"bar\"}";
string secret = "your_webhook_secret_key_here";
string signature = GenerateSignature(payload, secret);
Console.WriteLine($"Signature: {signature}");
// Verifying
string receivedSignature = "signature_from_header";
string expectedSignature = GenerateSignature(payload, secret);
Console.WriteLine(receivedSignature == expectedSignature ? "Valid" : "Invalid");
}
}
package main
import (
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
)
func generateSignature(payload, secret string) string {
key := []byte(secret)
h := hmac.New(sha256.New, key)
h.Write([]byte(payload))
return hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
}
func main() {
payload := `{"foo": "bar"}`
secret := "your_webhook_secret_key_here"
signature := generateSignature(payload, secret)
fmt.Println("Signature:", signature)
// Verifying
receivedSignature := "signature_from_header"
expectedSignature := generateSignature(payload, secret)
if receivedSignature == expectedSignature {
fmt.Println("Valid")
} else {
fmt.Println("Invalid")
}
}
import hmac
import hashlib
def generate_signature(payload: str, webhook_secret_key: str) -> str:
return hmac.new(
webhook_secret_key.encode('utf-8'),
payload.encode('utf-8'),
hashlib.sha256
).hexdigest()
# Example usage
payload = '{"foo": "bar"}'
webhook_secret_key = 'your_webhook_secret_key_here'
signature = generate_signature(payload, webhook_secret_key)
print('Signature:', signature)
# Verifying
received_signature = request.headers.get('HTTP-WEBHOOK-SIGNATURE')
expected_signature = generate_signature(request.get_data(as_text=True), webhook_secret_key)
if received_signature == expected_signature:
print("Valid")
else:
print("Invalid")
Note: Always use the raw request body for signature verification. Any modification (e.g., parsing and re-stringifying JSON) may result in signature mismatch.
Testing Guide: How to Verify HTTP Signature
1. Capture Webhook Request
-
Open the request log.
-
Copy the Raw Body JSON payload from the webhook request.
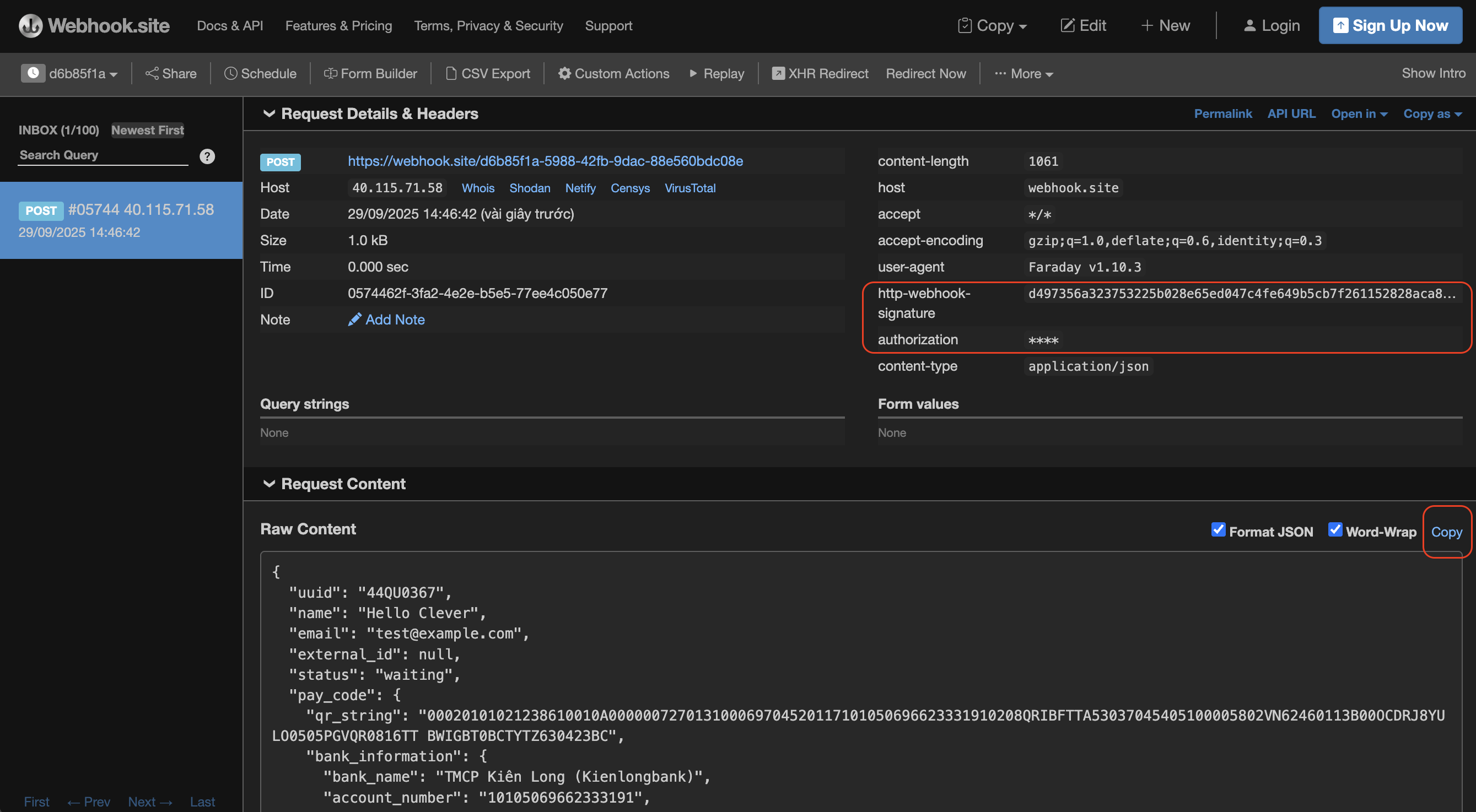
Example:
{
"uuid": "44QU0367",
"name": "Hello Clever",
"email": "test@example.com",
"external_id": null,
"status": "waiting",
"pay_code": {
"qr_string": "00020101021238610010A000000727013100069704520117101050696623331910208QRIBFTTA53037045405100005802VN62460113B00OCDRJ8YULO0505PGVQR0816TT BWIGBT0BCTYTZ630423BC",
"bank_information": {
"bank_name": "TMCP Kiên Long (Kienlongbank)",
"account_number": "101050696623331",
"account_name": "AABB",
"branch_name": "TP.Hồ Chí Minh",
"description": "Test Payin",
"swift_code": "KLBKVNVX"
},
"message": "Approved by financial institution"
},
"currency": "VND",
"amount": "10000.0",
"total": "10000.0",
"paid_amount": "10000.0",
"is_refundable": false,
"payment_method": "vn_vietqr_vnd",
"expired_at": "2025-12-23T06:00:00.000+0000",
"webhook_notification": {
"endpoint_url": "https://webhook.site/d6b85f1a-5988-42fb-9dac-88e560bdc08e",
"authorization_header": "****"
},
"status_text": "Payment has been approved, awaiting funds to settle",
"description": "Test Payin",
"gst": false,
"gst_amount": 0,
"pay_by": "2025-09-29T07:46:31.300+0000",
"sender_details": null,
"stage": "normal_stage"
}
2. Generate Hash via SHA256 Tool
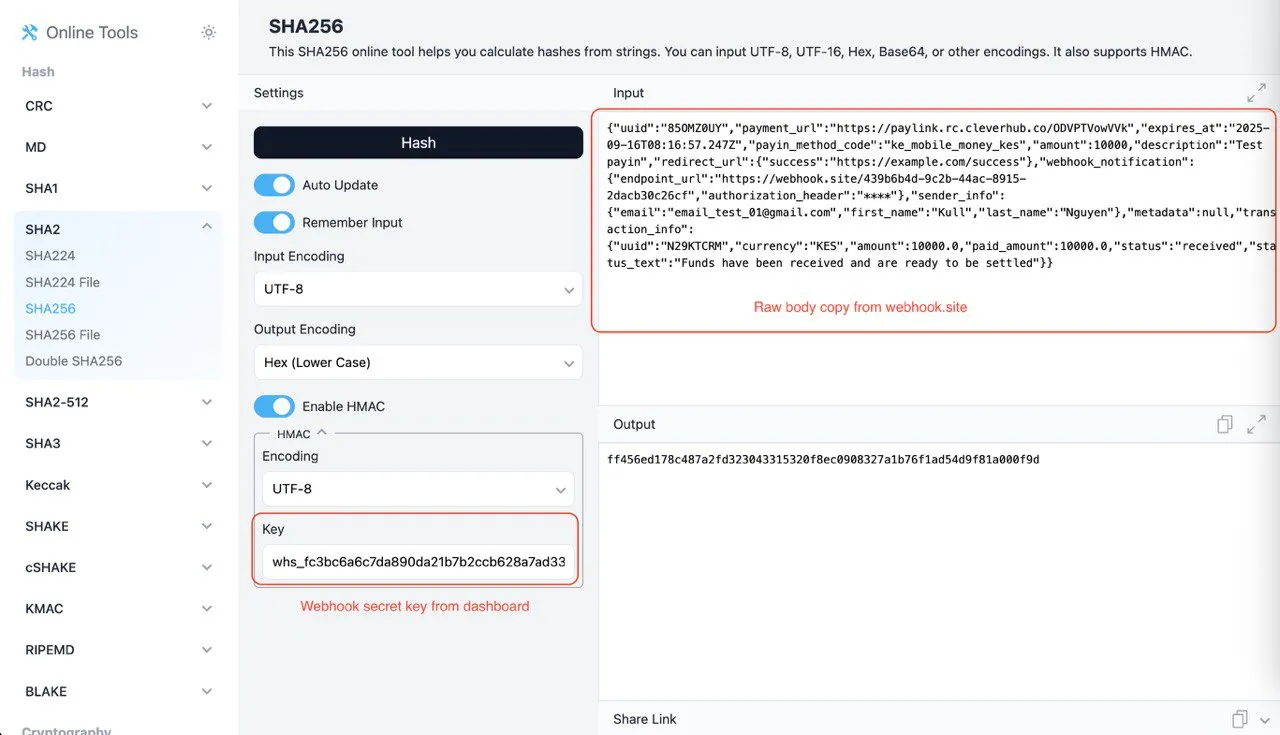
- Visit this website (example testing).
- Paste the Raw Body JSON into the Input box.
- Enable HMAC option.
- Enter your Webhook Secret Key in the Key field.
- Ensure:
- Input Encoding:
UTF-8 - Output Encoding:
Hex (Lower Case)
- Input Encoding:
- Copy the generated hash from the Output box.
3. Compare with Request Header
-
In the webhook request headers, locate the header:
http-webhook-signature: ff456ed178c487a2fd323043315320f8ec0908327a1b76f1ad54d9f81a000f9d -
Compare the generated hash (from SHA256 tool) with the value in http-webhook-signature.
✅ If they match → Signature is valid.
❌ If they differ → The request may be tampered with or key mismatch.
Example
-
Generated HMAC (tool):
ff456ed178c487a2fd323043315320f8ec0908327a1b76f1ad54d9f81a000f9d -
Webhook Header:
http-webhook-signature: ff456ed178c487a2fd323043315320f8ec0908327a1b76f1ad54d9f81a000f9d -
✅ Match → Valid Request.
Security Best Practices
- Keep your Webhook Secret Key secure and never expose it publicly.
- Always verify the signature before processing the webhook payload.